Maximum temperature for corten steel
In the realm of structural materials, corten steel, known also as weathering steel, has garnered considerable popularity due to its unique aesthetic appeal and remarkable durability. However, to ensure the preservation of its structural integrity and longevity, it becomes imperative to comprehend the maximum temperature limits that corten steel can withstand. Numerous factors come into play when determining this threshold.
Factors affecting the maximum temperature
1. Chemical composition of corten steel
The chemical composition of corten steel, particularly the presence of elements such as copper, chromium, and nickel, exerts a significant influence on its capacity to endure high temperatures. These alloying elements serve to enhance the steel’s resistance against the corrosive forces of oxidation, thus rendering it eminently suitable for outdoor applications.
2. Thickness of corten steel
The thickness of corten steel also assumes a pivotal role in ascertaining its maximum temperature limit. Thicker sections of steel generally exhibit a greater capacity to withstand elevated temperatures without succumbing to significant deformation or loss of structural integrity.

3. Exposure to atmospheric conditions
The atmospheric conditions to which corten steel is subjected can exert a profound impact on its maximum temperature limit. When exposed to the elements, corten steel develops a protective layer of rust, which acts as a formidable barrier against further corrosion. Nevertheless, prolonged exposure to aggressive environments or high levels of pollutants can expedite the process of corrosion and diminish the steel’s ability to endure high temperatures.
Maximum temperature limit for corten steel
1. Industry standards and recommendations
Industry standards and recommendations furnish invaluable guidelines concerning the maximum temperature limits of corten steel in various applications. These standards take into account a multitude of factors, including the intended use, structural design, and safety requirements, thereby ensuring the steel’s optimal performance within specific temperature conditions.
2. Effects of exceeding the maximum temperature limit
The consequences of surpassing the maximum temperature limit of corten steel are dire, exerting a deleterious impact on both its structural integrity and aesthetic allure. Elevated temperatures can precipitate accelerated corrosion, loss of strength, distortion, and even catastrophic failure of the steel components. It is of paramount importance to adhere scrupulously to the recommended maximum temperature limits, thereby obviating any compromise to the performance and longevity of corten steel structures.
Applications and usage scenarios
1. Common uses of corten steel
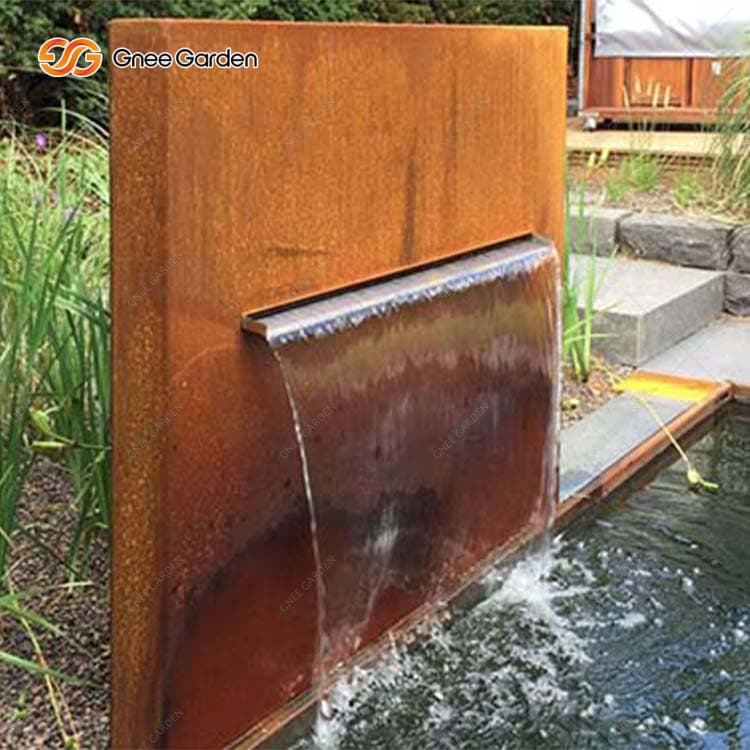
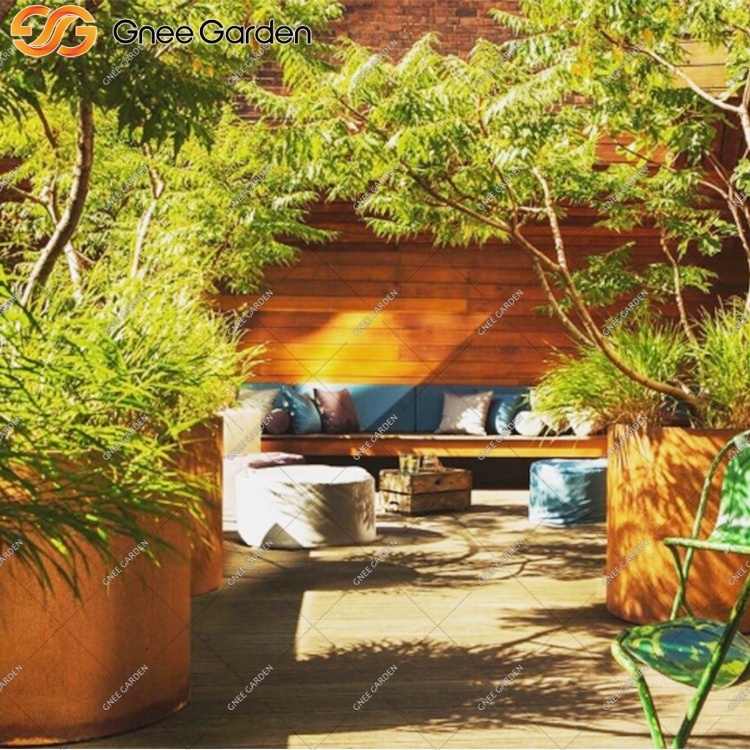
Corten steel finds itself employed in a myriad of industries, spanning architecture, construction, landscaping, and outdoor art installations. Its distinctive weathered appearance and formidable resistance to atmospheric corrosion render it an ideal choice for building facades, bridges, retaining walls, sculptures, and decorative features.

2. Maximum temperature considerations for specific applications
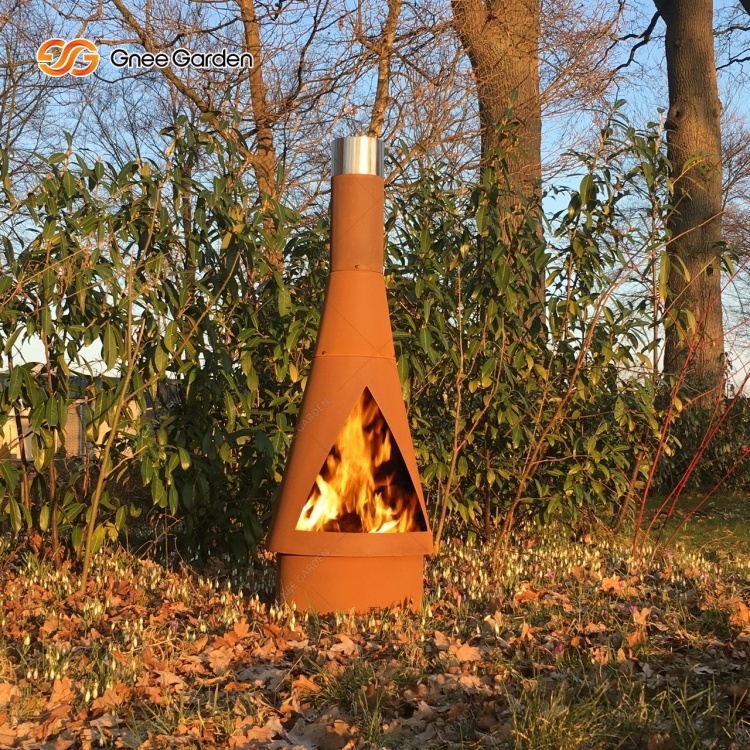
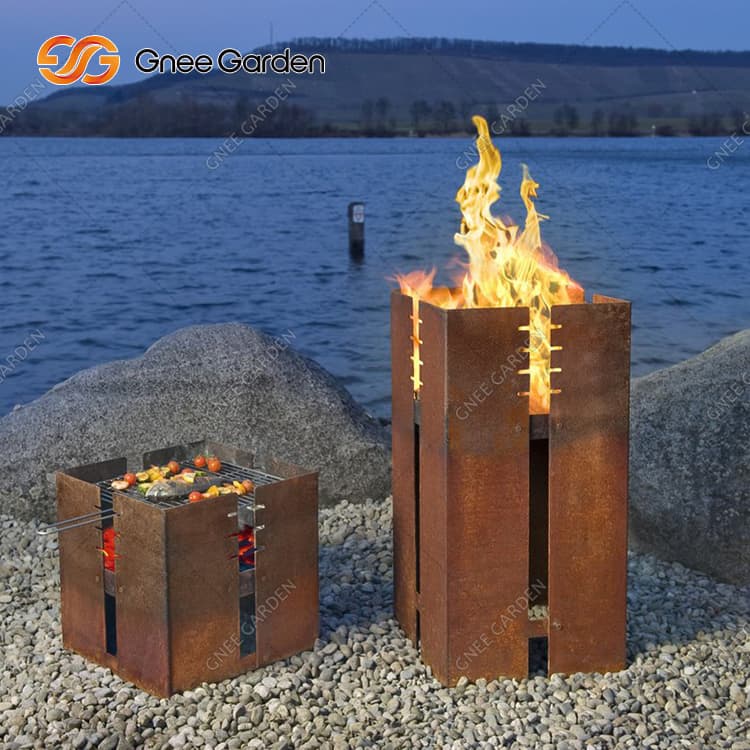
Specific applications of corten steel necessitate meticulous consideration of the maximum temperature limits. For instance, in architectural projects where corten steel is exposed to intense heat sources such as fire pits or exhaust vents, it becomes imperative to ascertain that the steel possesses the requisite fortitude to withstand the associated temperatures without compromising its structural integrity or aesthetic allure.
Precautions and maintenance
1. Precautions to avoid exceeding the maximum temperature
To avert the peril of surpassing the maximum temperature limits of corten steel, certain precautions ought to be observed. These may encompass judicious design considerations, insulation or heat shielding measures, and the avoidance of direct exposure to excessive heat sources or prolonged high-temperature environments.
2. Maintenance practices to ensure longevity of corten steel structures
The preservation of corten steel structures assumes paramount importance in guaranteeing their longevity. Regular inspection, cleaning, and the application of protective coatings serve to mitigate the corrosive forces of nature and extend the lifespan of the steel. It is essential to adhere diligently to the manufacturer’s recommendations and seek the counsel of experts regarding appropriate maintenance practices.
Frequently Asked Questions about Maximum Temperature for Corten Steel
What factors affect the maximum temperature that corten steel can withstand?
The maximum temperature limit of corten steel is influenced by factors such as its chemical composition, thickness, and exposure to atmospheric conditions.
How does the chemical composition of corten steel affect its maximum temperature limit?
The presence of elements like copper, chromium, and nickel in corten steel enhances its resistance to high temperatures and corrosion.
Does the thickness of corten steel affect its maximum temperature limit?
Thicker sections of corten steel generally have a greater capacity to withstand elevated temperatures without losing structural integrity.
What role does exposure to atmospheric conditions play in determining the maximum temperature limit of corten steel?
Corten steel forms a protective layer of rust when exposed to the elements, which helps it resist corrosion. However, prolonged exposure to aggressive environments or high levels of pollutants can reduce its ability to endure high temperatures.
Are there industry standards and recommendations for the maximum temperature limit of corten steel?
Yes, industry standards and recommendations provide guidelines for the maximum temperature limits of corten steel in different applications, considering factors like intended use, structural design, and safety requirements.
What are the consequences of exceeding the maximum temperature limit of corten steel?
Exceeding the maximum temperature limit can lead to accelerated corrosion, loss of strength, distortion, and even catastrophic failure of corten steel components.
What are some common uses of corten steel?
Corten steel is commonly used in architecture, construction, landscaping, and outdoor art installations. It is often used for building facades, bridges, retaining walls, sculptures, and decorative features.